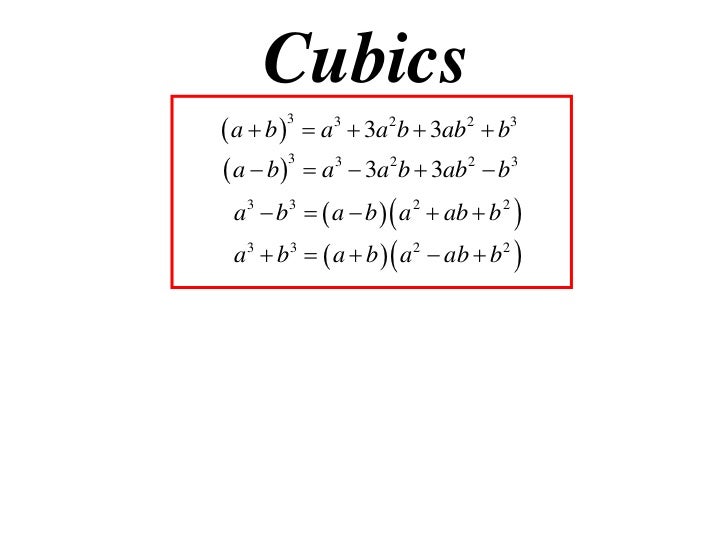
[新しいコレクション] (a-b)^3 263851-A b 3 4 and 8a+5b=22 then
Complex Numbers Complex numbers are used in alternating current theory and in mechanical vector analysis;Factorise 1 2 5 − 8 x 3 − 2 7 y 3 − 9 0 x y using the identity a 3 b 3 c 3 − 3 a b c = 2 1 (a b c) (a − b) 2 (b − c) 2 (c − a) 2 View solution View moreA > B find A and B In ∆ABC, rightangled at B, if tan A = 1/√3 find the value of (i) sin A cos C cos A sin C

Solution What Is The Equivalent Expansion Of The Cube Of A Binomial A B 3
A b 3 4 and 8a+5b=22 then
A b 3 4 and 8a+5b=22 then-If tan (A B) = √3 and tan (A – B) = \(\frac{1}{\sqrt 3}\) 0° < A B ≤ 90°;(a b)^3 can be written as, (a b) * (a b) * (a b) Let's multiply the first two terms (a b) * (a b) * (a b) a*a a*b b*a
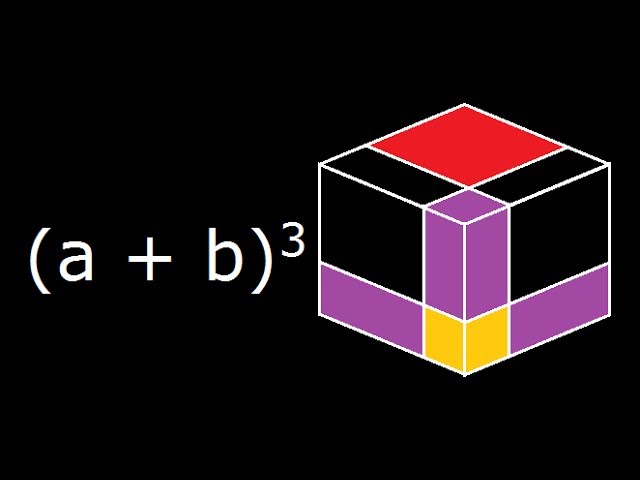


A B 3 A Plus B Cube Algebra Identity Geometrical Explanation And Derivation Youtube
0° < A B ≤ 90°;Math a^3 b^3 = (a b)(a^2 b^2 ab) /math Lets try to derive this expansion from the expansion of math (a b) ^ 3 /math We have, math(a b) ^ 3 = a^3A > B, find A and B Given that Our equations are A B = 60° (1) A – B = 30° (2) Adding (1) and (2) A B A – B = 60° 30° 2A = 90° A = (90°)/2 A = 45° Putting A = "45°" in (1) A B = 60° 45° B = 60° B = 60° − 45° B = 15° Hence A = 45° , B = 15°
Any person that is determined by the Commission, in accordance with paragraph (3) or (4) of section 503(b) of this title, to have violated this subsection with the intent to cause such violation shall be liable to the United States for a forfeiture penalty pursuant to section 503(b)(1) of this titleParagraph (5) of section 503(b) of this title shall not apply in the case of a violation of\(=> (abc)^3 = \\a^3 b^3 c^3 6abc 3ab (ab) 3ac (ac) 3bc (bc) \) (abc)^3 Verifications Need to verify \( (a b c)^ 3 \) formula is right or wrong put the value of a = 1, b=2 and c=3 put the value of a and b in the LHS \( (abc)^3 = (123)^3 \) \( 6^3 = 216 \) put the value of a and b in the RHSExample Solve 8a 3 27b 3 125c 3 – 90abc Solution This proceeds as Given polynomial (8a 3 27b 3 125c 3 – 90abc) can be written as (2a) 3 (3b) 3 (5c) 3 – 3(2a)(3b)(5c) And this represents identity a 3 b 3 c 3 3abc = (a b c)(a 2 b 2 c 2 ab bc ca) Where a = 2a, b = 3b and c = 5c Now apply values of a, b and c on the LHS of identity ie a 3 b 3 c 3
The Formula is given below (a b c)³ = a³ b³ c³ 3 (a b) (b c) (a c) Explanation Let us just start with (abc)² = a² b² c²2ab2bc2ca\(=> (ab)^3 = a^3 ab^2 – 2a^2 b – ba^2 – b^3 2ab^2 \) Arrange \(=> (ab)^3 = a^3 ab^2 2ab^2 – 2a^2 b – ba^2 – b^3 \) \(=> (ab)^3 = a^3 3 ab^2 – 3a^2 b – b^3 \) Also Write \(=> (ab)^3 = a^3 – b^3 3 ab (ba) \) (AB)^3 Verifications Need to verify \((ab)^3\) formula is right or wrong put the value of a = 5Multiplying out by #ab# gives us #a^2b^2=3ab# #a^23abb^2=0# #a=(3bsqrt(9b^24b^2))/2# #a=(3bsqrt(13b^2))/2# #a=(3bbsqrt(13))/2# #a=(b(3sqrt13))/2# #a^3
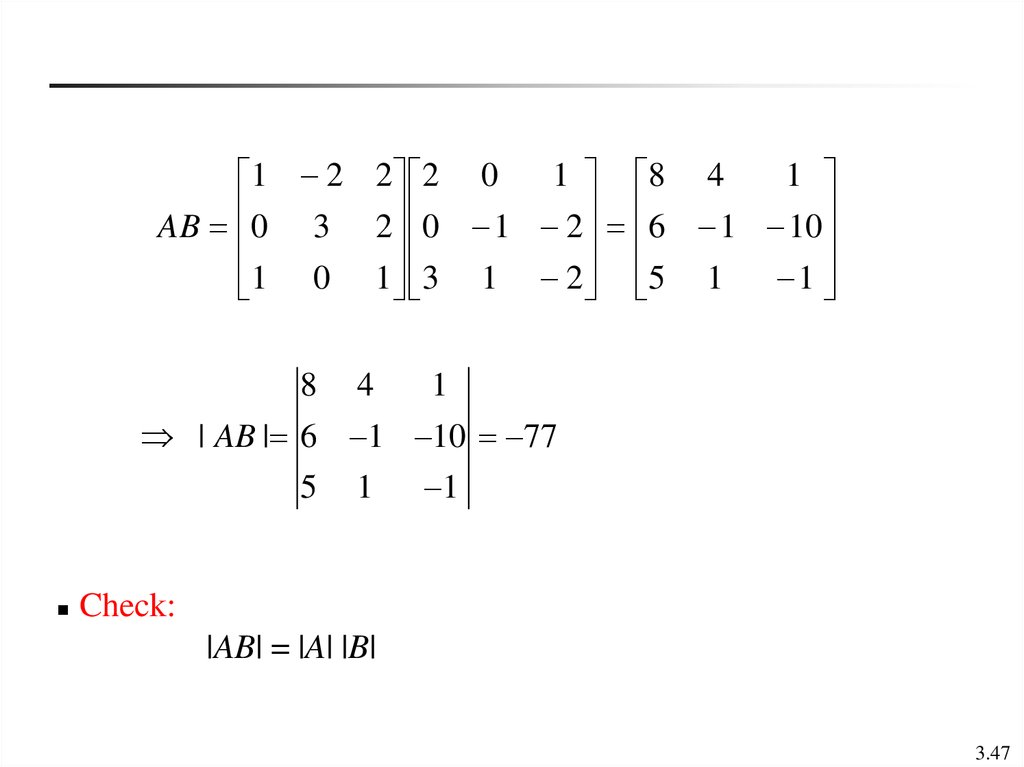


Determinants Online Presentation



Algebra Formulas A B 3 A B 2 A B C 3 A 3 B 3 Algebra Formulas Algebra Notes Algebra Help
(ab)^3 (a b)^3 ( a b ) ^ 3 ( a b ) ^ 3 and this will go on for ever Just write the expression on your page and see the miracle Source(s) my self 0 0 Paul Lv 7 7 years ago a^3 3a^2b 3ab^2 b^3 0 0 Anonymous 7 years ago (ab)^3=a^3 3*a^2*b3*a*b^2b^3Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreHttp//wwwfreemathvideoscom In this video playlist I will show you the basics for polynomial functions We will start with factoring polynomial equations



Factorise A B 3 B C 3 C A 3 Thanks Math Polynomials Meritnation Com
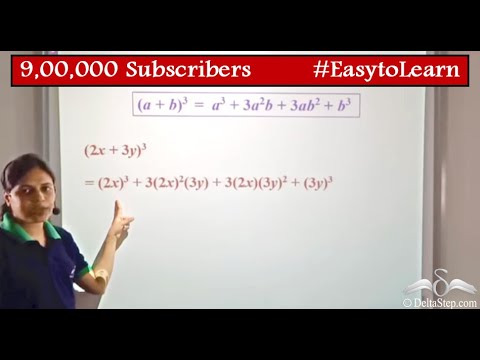


Special Identities A B 3 A B 3 Youtube
Discrete Data Sets Mean, Median and Mode Values Calculate arithmetic meanA 3 / b 3 = (a / b) 3 (16) 1 / a 3 = (1 / a) 3 = a3 (17) (a 2) 3 = a 2 3 = (a 3) 2 = a 6 (18) a 3 b 3 = (a b) (a 2 a b b 2) (19) a 3 b 3 = (a b) (a 2 a b b 2) () (a b) 3 = a 3 3 a 2 b 3 a b 2 b 3 (21) (a b) 3 = a 3 3 a 2 b 3 a b 2 b 3 (22) a 1/2 a 1/2 = a (23)What is (ab)^3 Formula?



Partitioning A Segment In A Given Ratio
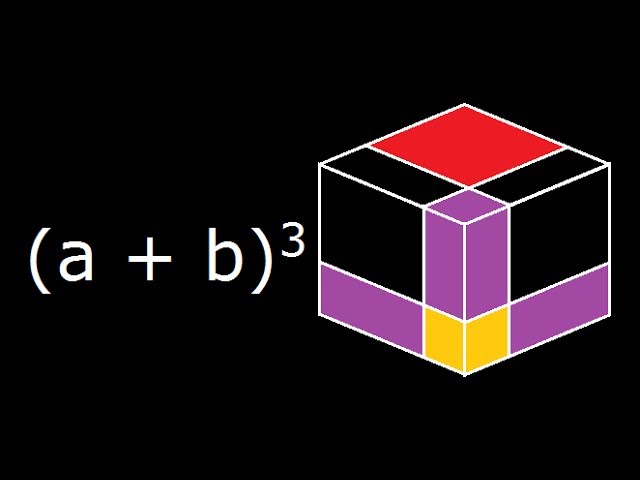


A B 3 A Plus B Cube Algebra Identity Geometrical Explanation And Derivation Youtube
You have 5 a ⋅ b = 3 b ⋅ b − 2 a ⋅ a 1 5 a ⋅ b = − 7 b ⋅ b − 2 a ⋅ a so subtract the 2nd equation from the first to get − 1 0 a ⋅ b = 1 0 b ⋅ b ⇒ b ⋅ b = − a ⋅ b Also 3 5 a ⋅ b = 2 1 b ⋅ b − 1 4 a ⋅ aWhen you divided by xab you threw away the root x=ab Just like in the equation t(t1)=t(2t5), if we cancel the t we are losing the root t=0 When you divided by x − a − b you threw away the root x = a bRelated Documents Binomial Theorem Binomial theorem for positive integers;



What Is The Answer Of This Formula A B 3 Mathematics Topperlearning Com O2bgc4vv


Simplify It A 3 A 3 Socratic
A b)2 = 1a2 2ab 1b2 (a b)3 = 1a3 3a2b 3ab2 1b3 How are binomial expansions related to Pascal's triangle?= a 3 b 3 3ab(a b) On solving it further we get a 3 b 3 3a 2 b 3ab 2 Hence, in this way we obtain the identity ie (a b) 3 = a 3 b 3 3ab(a b) = a 3 b 3 3a 2 b 3ab 2 Example 1 Solve (3a 2b) 3 Solution This proceeds as Given polynomial (3a 2b) 3 represents the identity (a b) 3 Where a = 3a and b = 2b Now#(ab)^3# is the same as #(ab)^2(ab)#, so if we write it in this way, it becomes a much easier problem to solve #(ab)^2# is the same as #(ab)(ab)#, and if we distribute the #a# and #b# to both terms, we'll get #a^22abb^2# We now have #(ab)(a^22abb^2)# Again, we can distribute the #a# and #b# to all terms to get #a^32a^2bab^2a^2b
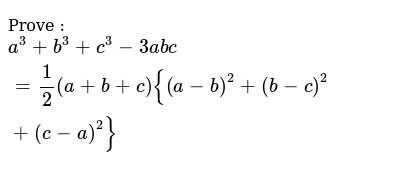


Prove A 3 B 3 C 3 3abc 1 2 A B C A B 2 B C 2 C A 2



Rogue Ab 3 Adjustable Bench Rogue Fitness
Summary (AB)^3 If you have any issues in the (AB)^3 formulas, please let me know through social media and mail A Plus B Whole Cube is most important algebra maths formulas for class 6 to 13Family of E Visa Holders If your I140 petition is approved, your spouse and unmarried children under the age of 21 may be eligible to apply for admission to the United States in 4 (spouse of a "skilled worker" or "professional") or EW4 (spouse of an "other worker") and 5 (child of a "skilled worker" or "professionalRelated Topics Mathematics Mathematical rules and laws numbers, areas, volumes, exponents, trigonometric functions and more ;



Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab



Expand Please A B 3 A B 3 Math Inverse Trigonometric Functions Meritnation Com
If a,b,c are all nonzero and a b c = 0, prove that a2/bc b2/ca c2/ab = 3 asked Sep 14, 18 in Class IX Maths by aditya23 ( 2,139 points) polynomialsYou have 5 a ⋅ b = 3 b ⋅ b − 2 a ⋅ a 1 5 a ⋅ b = − 7 b ⋅ b − 2 a ⋅ a so subtract the 2nd equation from the first to get − 1 0 a ⋅ b = 1 0 b ⋅ b ⇒ b ⋅ b = − a ⋅ b Also 3 5 a ⋅ b = 2 1 b ⋅ b − 1 4 a ⋅ aSummary (AB)^3 If you have any issues in the (AB)^3 formulas, please let me know through social media and mail A Plus B Whole Cube is most important algebra maths formulas for class 6 to 13



Formula Of Ab 3 Is Please Answer This Brainly In



Simplify The Expression And Find Its Value When A 5 And B 3 T
Conditioning on an event Kolmogorov definition Given two events A and B from the sigmafield of a probability space, with the unconditional probability of B being greater than zero (ie, P(B)>0), the conditional probability of A given B is defined to be the quotient of the probability of the joint of events A and B, and the probability of B (∣) = (∩) (),Get the list of basic algebra formulas in Maths at BYJU'S Stay tuned with BYJU'S to get all the important formulas in various chapters like trigonometry, probability and so onA list of the most commonly used algebra formulas Exponents, polynomials, etc A good quickreference list or formula study guide



3 C B


What Is The Correct Formula Of Math A B 3 Math Quora
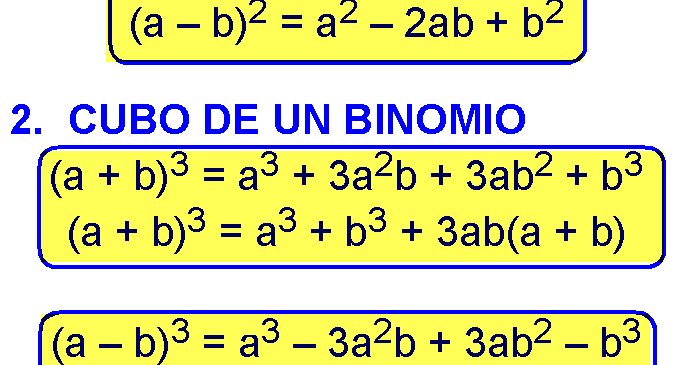
MATHEMATICAL FORMULAE Algebra MATHEMATICAL FORMULAE Algebra 1 (ab)2=a22abb2;a2b2=(ab)2−2ab 2 (a−b)2=a2−2abb;a2b2=(a−b)22ab 3 (abc)2=a2b2c22(abbcca) 4 (ab)3=a3b33ab(ab);a3b3=(ab)−3ab(ab) 5Math a^3 b^3 = (a b)(a^2 b^2 ab) /math Lets try to derive this expansion from the expansion of math (a b) ^ 3 /math We have, math(a b) ^ 3 = a^3(a 3 3a 2 b 3ab 2 b 3)(ab) = a 4 4a 3 b 6a 2 b 2 4ab 3 b 4 The calculations get longer and longer as we go, but there is some kind of pattern developing That pattern is summed up by the Binomial Theorem



Let Abc Is A Right Angled Triangle In Which Ab 3 Cm And 4 Cm And Abc 90 O The Three Charges 15 12 And Esu Are Placed
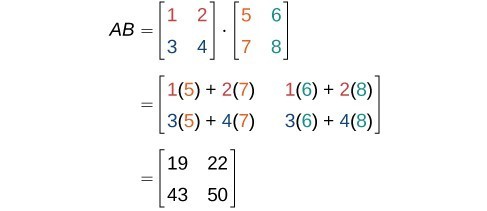


Finding The Product Of Two Matrices College Algebra
(ab) 2 = a 2 2ab b 2 (ab)(cd) = ac ad bc bd a 2 b 2 = (ab)(ab) (Difference of squares) a 3 b 3 = (a b)(a 2 ab b 2) (Sum and Difference of CubesTranscript Ex , 3 If tan (A B) = √3 and tan (A – B) = 1/√3 ;2 See answers afmill01 afmill01 Pascal triangles gives us the coefficients for an expanded binomial of the form (ab)n,where n is now the row of the triangle


Http Www Wfisd Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 490 Tstrv2pg5 Pdf



A B 3 A B 3 Formula
Factoring a 3 b 3 An expression of the form a 3 b 3 is called a difference of cubes The factored form of a 3 b 3 is (a b)(a 2 ab b 2) (a b)(a 2 ab b 2) = a 3 a 2 b a 2 b ab 2 ab 2 b 3 = a 3 b 3For example, the factored form of 27x 3 8 (a = 3x, b = 2) is (3x 2)(9x 2 6x 4) Similarly, the factored form of 125x 327y 3 (a = 5x, b = 3y) is (5x 3y)(25x 2Let's find it ourselves!Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge and



What Is The Formula Of Math A B 3 Math Quora



Ex 12 3 10 Simplify Expression And Find Its Value If A 5 B 3
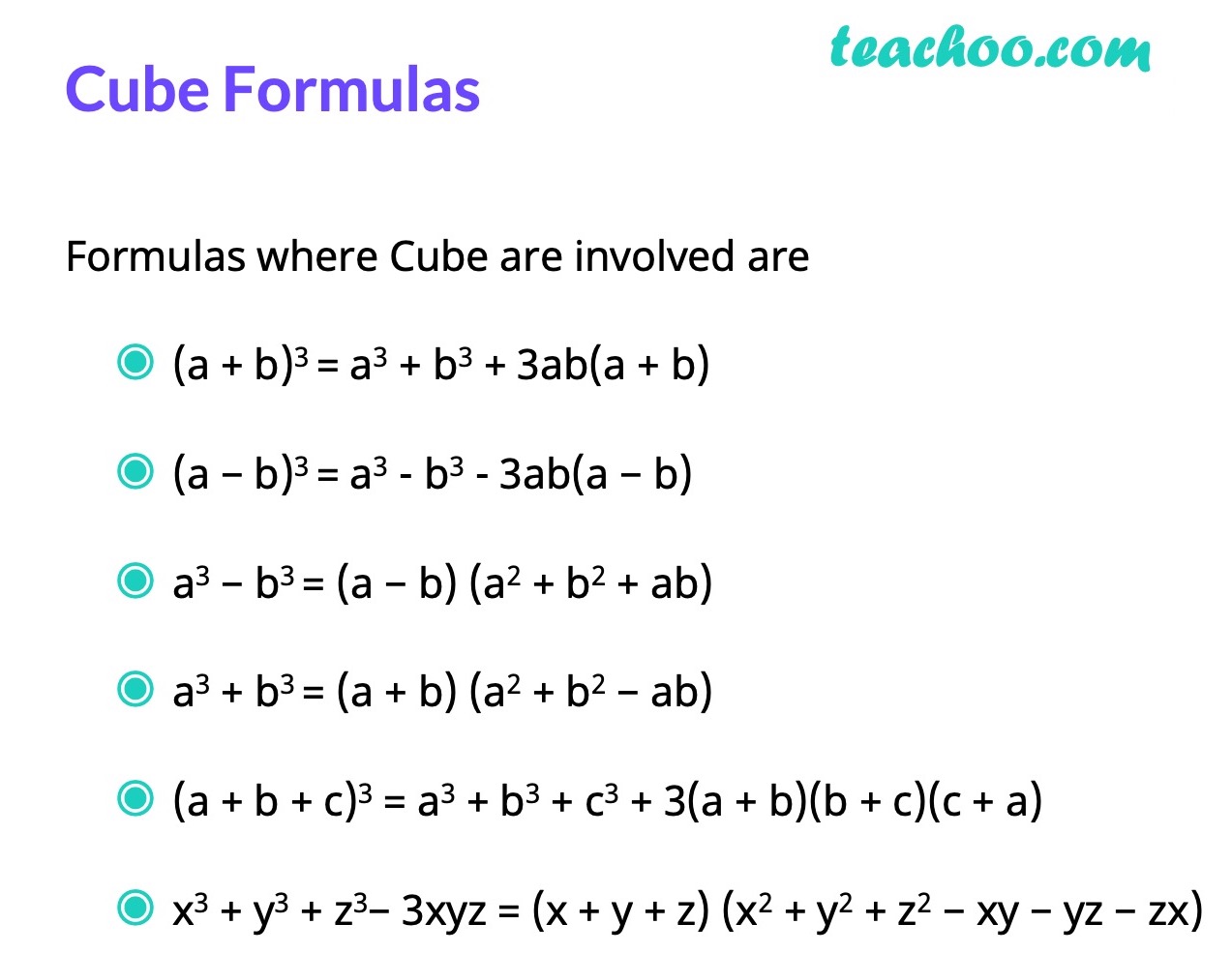
Cube Formulas (a b) 3 = a 3 b 3 3ab (a b) (a − b) 3 = a 3 b 3 3ab (a b) a 3 − b 3 = (a − b) (a 2 b 2 ab) a 3 b 3 = (a b) (a 2 b 2 − ab) (a b c) 3 = a 3 b 3 c 3 3 (a b) (b c) (c a) a 3 b 3 c 3 − 3abc = (a b c) (a 2 b 2 c 2 − ab − bc − ac) If (a b c) = 0,To simplify the above expressions, start by expanding the binomials Note that we can expand the (ab)^3 , (bc)^3 , and (ca)^3 using the special product formulas for a cube of a binomialA^3 3a^2b 3ab^2 b^3 Use the Binomial expansion (note the exponents sum to the power in each term) (xy)^3 = _3C_0x^3y^0 _3C_1x^2y^1 _3C_2x^1y^2 _3C_3x^0y^3



If A B 5 And Ab 6 Then Find The Value Of A 3 B 3



Binomial Theorem Formula
Factoring a 3 b 3 An expression of the form a 3 b 3 is called a difference of cubes The factored form of a 3 b 3 is (a b)(a 2 ab b 2) (a b)(a 2 ab b 2) = a 3 a 2 b a 2 b ab 2 ab 2 b 3 = a 3 b 3For example, the factored form of 27x 3 8 (a = 3x, b = 2) is (3x 2)(9x 2 6x 4) Similarly, the factored form of 125x 327y 3 (a = 5x, b = 3y) is (5x 3y)(25x 2Solution Steps ( 3 a b ) \cdot ( a 2 b ) (3a b) ⋅ (a − 2b) Apply the distributive property by multiplying each term of 3ab by each term of a2b Apply the distributive property by multiplying each term of 3a b by each term of a −2b 3a^ {2}6abba2b^ {2} 3a2 − 6ab ba − 2b2 Combine 6ab and ba to get 5abA^3b^3 Formula (ab)^2 (abc)^2 (a – b)^3 = a^3 – 3a^2b 3ab^2 – b^3 a^3 – b^3 = (a – b)(a^2 ab b^2)



Solved A 2 3 1 6 1 2 B 4 5 3 0 1 2 Find Ab A Chegg Com



Rogue Ab 3 Adjustable Bench Rogue Fitness
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreRegister for FREE at http//deltastepcom or download our mobile app https//bitly/3akrBoz to get all learning resources as per ICSE, CBSE, IB, Cambridge &Convair complied by replacing the wings on a 6F with swept wings, from which were suspended eight Pratt & Whitney XJ57P3 jet engines The result was the 6G, later renamed the Convair YB60 The YB60 was deemed inferior to Boeing's YB52, and the project was terminated


3 B Www Dingjisc Com


Www Jstor Org Stable
Answer a³ 3a²b 3ab² b³ Show more Rameshwar Lv 7 1 decade ago ( ab)^3 = ( a b)^2 (ab) = ( a^2 2ab b^2) ( a b ) = a^3 3a^2b 3b^2a b^3 = a^3 3ab ( a b) b^3 ans in(ab) 2 = a 2 2ab b 2 (ab)(cd) = ac ad bc bd a 2 b 2 = (ab)(ab) (Difference of squares) a 3 b 3 = (a b)(a 2 ab b 2) (Sum and Difference of CubesTrong toán học sơ cấp, bảy hằng đẳng thức đáng nhớ là những đẳng thức cơ bản nhất mà mỗi người học toán cần phải nắm vững Các đẳng thức được chứng minh bằng phép nhân đa thức với đa thức Các hàng đẳng thức này nằm trong nhóm các hàng đẳng thức đại số cơ bản, bên cạnh nhiều hàng đẳng



Add A B 3 B A 3 A B 3



How To Determine Your Baby S Blood Type Using A Punnett Square
1) (a b)^3 = (a b)(a b)(a b) = (a*a b*a a*b b*b)(a b) = (a^2 ab ab b^2)(a b) = (a^2 2ab b^2)(a b) = a^2*a 2ab*a b^2*a a^2*b 2abRegister for FREE at http//deltastepcom or download our mobile app https//bitly/3akrBoz to get all learning resources as per ICSE, CBSE, IB, Cambridge &(abc) 3 a 3 b 3 c 3 We can choose three "a"'s for the cube in one way C(3,3)=1, or we can choose an a from the first factor and one from the second and one from the third, being the only way to make a3 The coefficient of the cubes is therefore 1 (It's the same for a, b and c, of course) 3a 2 b3a 2 c Next, we consider the a 2 terms We



Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Solubility S And Solubility Product Ksp



Factorise 250 A B 3 2 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 3dga2eee


Productos Notables Problemas Resueltos


What Is The Formula Of Math A B 3 Math Quora



Usb Cable Standard A B 3 Ft 1m Id 62 2 95 Adafruit Industries Unique Fun Diy Electronics And Kits


Euclid S Elements Book I Proposition 3



Dopl3r Com Memes Lmao These Are So True00 A B Ab Ab Ab 2 32 3 5 A3 A B Ab B2 A3 A B Ab



Solution What Is The Equivalent Expansion Of The Cube Of A Binomial A B 3
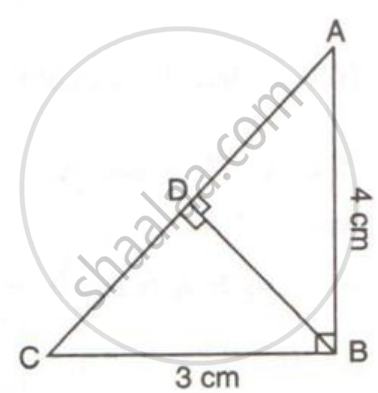


In The Given Figure Triangle Abc Is Right Angled At B D Is The Foot Of The Perpendicular From B To Ac Given That 3 Cm And Ab 4 Cm


If A B 3 And B2 29 Find The Value Of Ab Quora


Illustrations Of Formulas


Using Properties Of Determinants Prove That B 2 C 2 A 2 Ac Ac C 2 Ac A 2 Ab B 2 Ab Ab Ab Ac 3 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Algebra Formulas A B 3 A B 2 A B C 3 A 3 B 3 Teachoo


If A B 6 And Ab 8 Find A3 Polynomials Maths Class 9
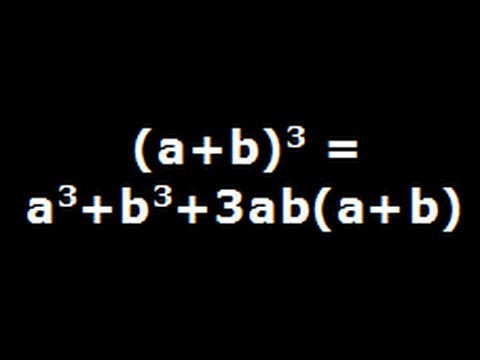


A Plus B Cube Algebra Identity Explained Step By Step Youtube



Lcm Of A 3 B 3 And A 4 B 4 Is



العلامة A B 3 الصور والأفكار



Eagsq Th0rtd2m


Derivation Of Formula For A B 3



Simplifying Radical Expressions
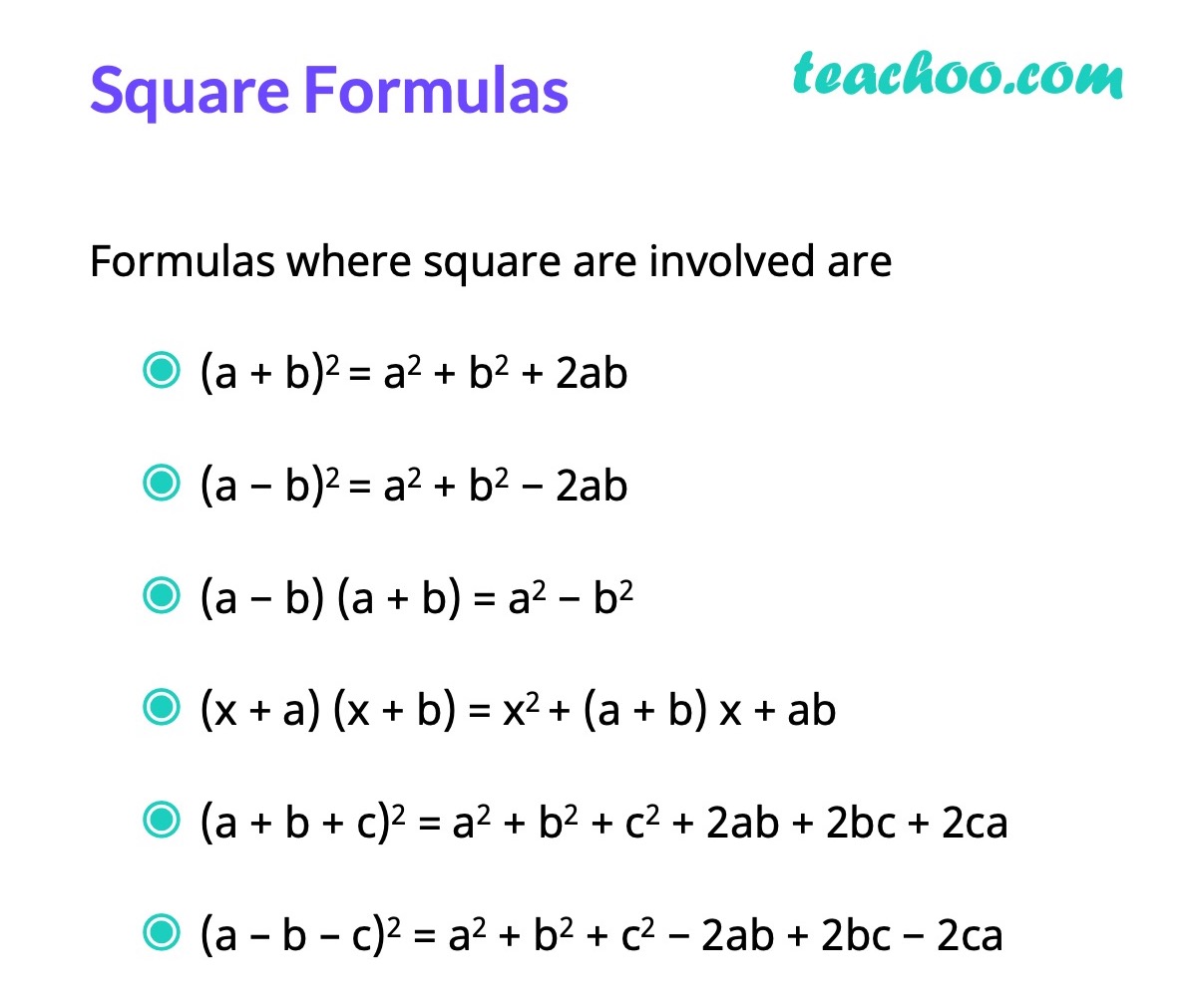


Algebra Formulas A B 3 A B 2 A B C 3 A 3 B 3 Teachoo


Prove That A B C 3 A3 C3 3 A B B C C A Studyrankersonline
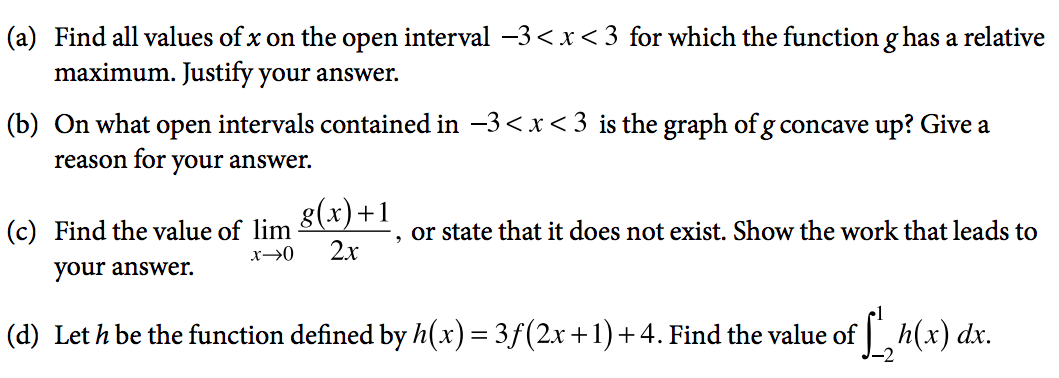


The Best Ap Calculus Ab Review Guide For 21 Albert Resources



If A B 3 And A 3 B 3 117 Then A B Is Youtube


Search Q A 5e2 2bb 5e2 Tbm Isch



Sennheiser Ab 3 Antenna Booster



Alpha Bita 3 Alpha 3 Beta 3 1 Fin F Quadratic Equation Te5voeff Mathematics Topperlearning Com


Q Tbn And9gcrswdldblxmiitn Ggstx6knbcgxw3sex0r673zeswoh Igfkvn Usqp Cau



Dl And Bm Are The Heights On Sides Ab And Ad Respectively Of Parallelogram Abcd If The Area Of The Parallelogram Is 1470 Cm 2 Ab 35 Cm And Ad


Prove That A B C 3 A3 C3 3 A B B C C A Polynomials Maths Class 9



Adjustable Roof Jack Base 3 Inch Ab 3 Hvac Express



If 1 1 1a B C A 3b 2c 3 A B B C C A A B C W H E R Ea B



Thermo Scientific Lab Vision Chromogranin A Ab 3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody 100ml 1mg Ml Unlabeled Purified Without Bsa And Azide Thermo Scientific Lab Vision Chromogranin A Ab 3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody Fisher Scientific



What Is The Correct Formula Of Math A B 3 Math Quora



Please Explain Formula Of A B 3 Math Cubes And Cube Roots Meritnation Com
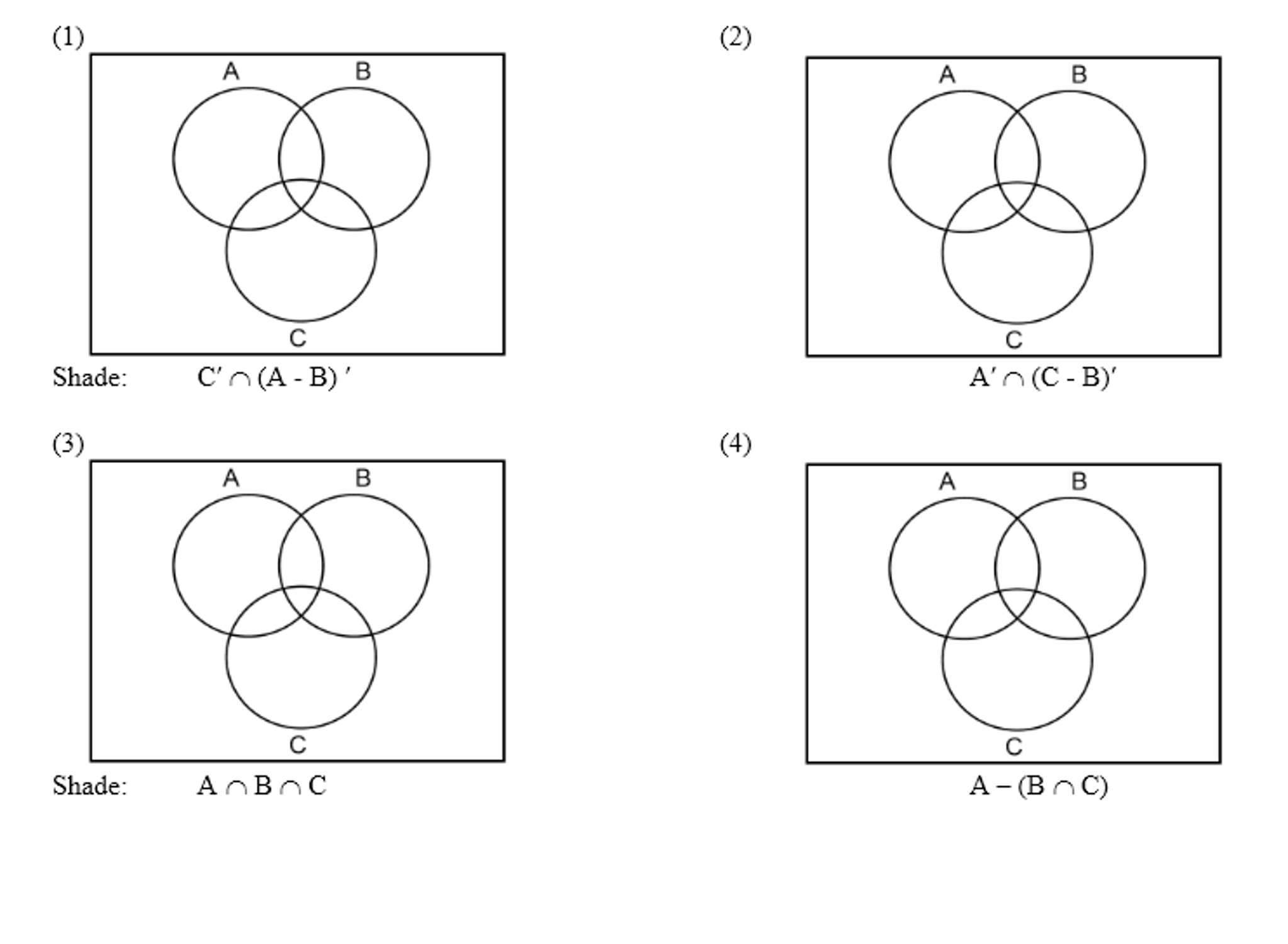


Solved 1 Shade C N A B 3 A N B N C Shade 2 4 N Chegg Com



Algebra The Greatest Mathematical Tool Of All This Is A Course In Basic Introductory Algebra Essential Prerequisites Ability To Work With Directed Ppt Download


What Is The Formula For Math A 3 B 3 Math Quora


What Is The Value Of A3 If A B B A 1 Quora
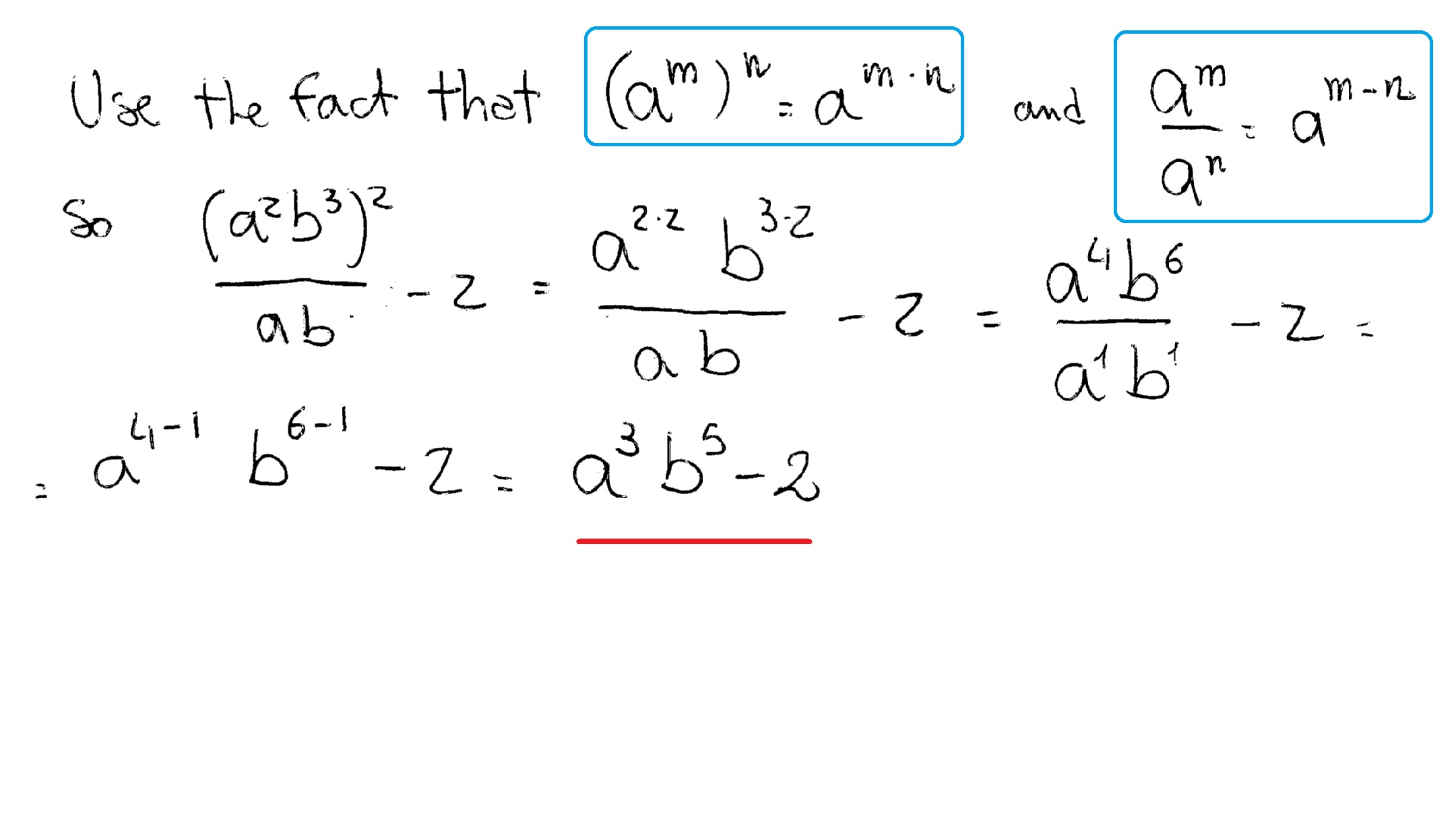


How Do You Simplify A 2 B 3 2 Ab 2 Socratic


Q Tbn And9gcsjdrnx7bzqtlocyzksajkrzoljxhqicxqu10lfrwznup Pf Ff Usqp Cau



If A B B A 1 Find A 3 B 3 Mathematics Topperlearning Com Xxfqewee



Unit 18 Vectors Geometric Proof Ppt Download



If A B C 5 And Ab Ca 10 Prove A 3 B 3 C 3 3abc 25 Mathematics Topperlearning Com 1zf53szz



Algebra Sleuth Proof That 1 2 Activity Education Com



Binomial Theorem
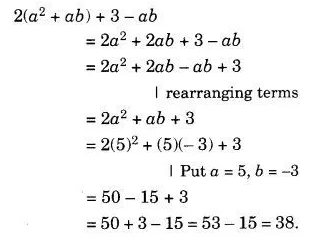


Simplify The Expression And Find Its Value When A 5 And B 3 2 Ab 3 Ab Cbse Class 7 Maths Learn Cbse Forum



Please Factories A B 3 8 A B 3 Brainly In



ब जगण त स त र Docx



Vsepr Theory Rules Application And Geometry Of Ab2 Ab3 And Ab4



Question Video Finding The Product Of Two Matrices Nagwa



Please Factories A B 3 8 A B 3 Brainly In



If A 2 B 2 9 And Ab 4 Find The Value Of 3 A B 2 2 A B 2 Brainly In



Aichi Ab 3 Wikipedia



Solved Find The Product Ab For A A 1 1 3 1 B Chegg Com



Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 4 Triangles Exercise 4 2 Access Pdf For Free



Find The Area Of A Quadrilateral Abcd In Which Ab 3 Cm 4 Cm Cd 4 Cm Da 5 Cm And Ac 5 Cm
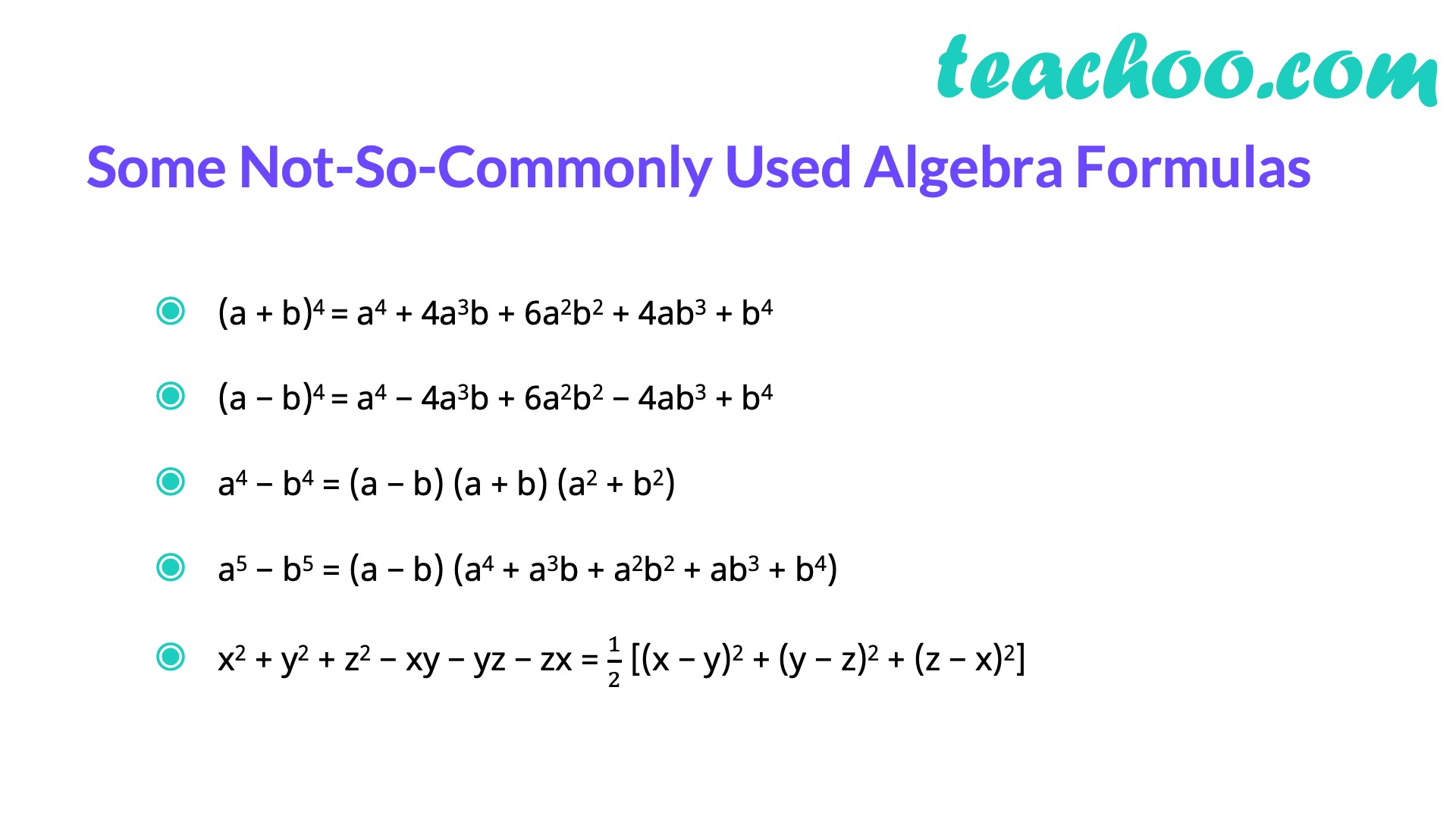


Algebra Formulas A B 3 A B 2 A B C 3 A 3 B 3 Teachoo


The Formula For A B 3 The Cube Of A Binomial Lunlun Com
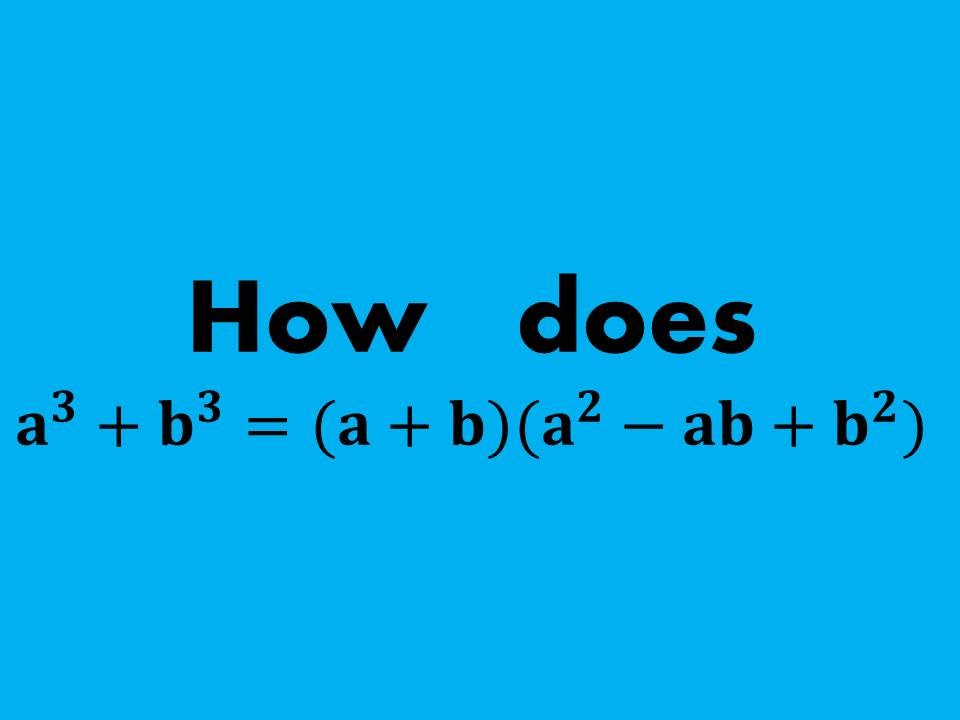


Proof How To Prove The Sum Of Two Cubes A 3 B 3 A B A 2 Ab B 2 Youtube



If A B C 11 And Ab Ca Then The Value Of The Expression A



Rogue Ab 3 Adjustable Bench Rogue Fitness



Ex 16 1 5 Find The Values Of Letters A B X 3 C A B
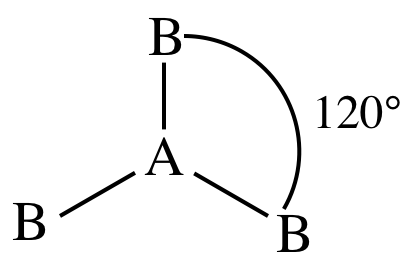


Top Of Page Periodic Table Andover S Chem 300 Accelerated Honors Chemistry Table Of Contents Chapter 11 Molecular Geometry Polarity Of Molecules And Advanced Bonding Theory Section 11 1 Molecular Geometry Using Vsepr Theory To



Simple Proof Of A B A 3a B 3ab B A B 3ab A B And A B A 3a B 3ab B A B 3ab A B Youtube
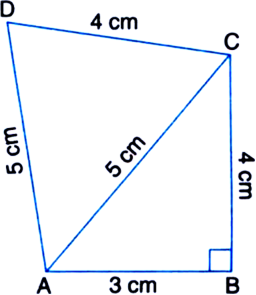


Find The Area Of A Quadrilateral Abcd In Which Ab 3 Cm 4 Cm Cd 4 Cm Da 5 Cm And Ac 5 Cm From Mathematics Heron S Formula Class 9 Meghalaya Board


Identites Remarquables De Degre Superieur A 2


What Is The Formula Of Math A 3 B 3 Math Quora


Category Math Help Softmath Blog


Search Q A 5e2 2bb 5e2 Formula Tbm Isch
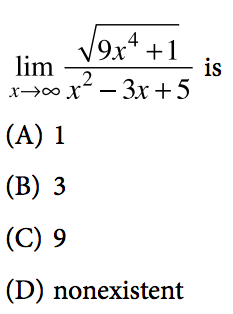


The Best Ap Calculus Ab Review Guide For 21 Albert Resources



Rogue Ab 3 Adjustable Bench Rogue Fitness
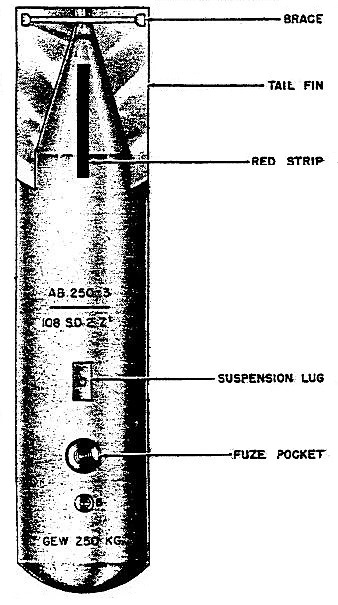


Ab 250 3 Wikipedia
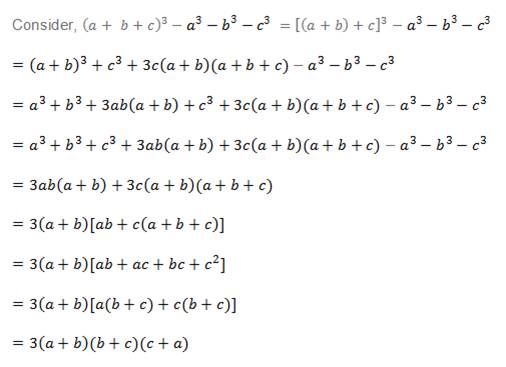


Prove That A B C 3 A3 C3 3 A B B C C A Polynomials Maths Class 9


コメント
コメントを投稿